 |  |
|
Updated:
Major infectious diseases in Thailand
  Major infectious diseases in Thailand include bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis, Cocvid-19, dengue fever, malaria, Japanese encephalitis, rabies, and leptospirosis.
A study by the health ministry and Britain's Wellcome Trust released in September 2016 found that an average of two people die every hour from multi-drug resistant bacterial infections in Thailand. That death rate is much higher than in Europe. The improper use of antibiotics for humans and livestock has led to the proliferation of drug-resistant microorganisms. In Thailand, antibiotics are freely available in pharmacies without a prescription and even in convenience stores.
In November 2016, Thailand announced its intent to halve antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) infections by 2021, joining the global battle against superbugs. But because Thailand remains Thailand, nothing really successful was ever initiated.
BBC News: Millions are dying from drug-resistant infections, global report says
Covid-19
 Coronaviruses are a large family of different viruses and have coexisted with humans for a long time.
The Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The first known infections from SARS-CoV-2 were discovered in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The original source of viral transmission to humans remains unclear, as does whether the virus became pathogenic before or after the spillover event. Because many of the early infectees were workers at the Huanan Seafood Market, it has been suggested that the virus might have originated from the market. However, other research indicates that visitors may have introduced the virus to the market, which then facilitated rapid expansion of the infections.
COVID-19 affects different people in different ways. Most infected people will develop mild to moderate illness and recover without hospitalization.
Most common symptoms:
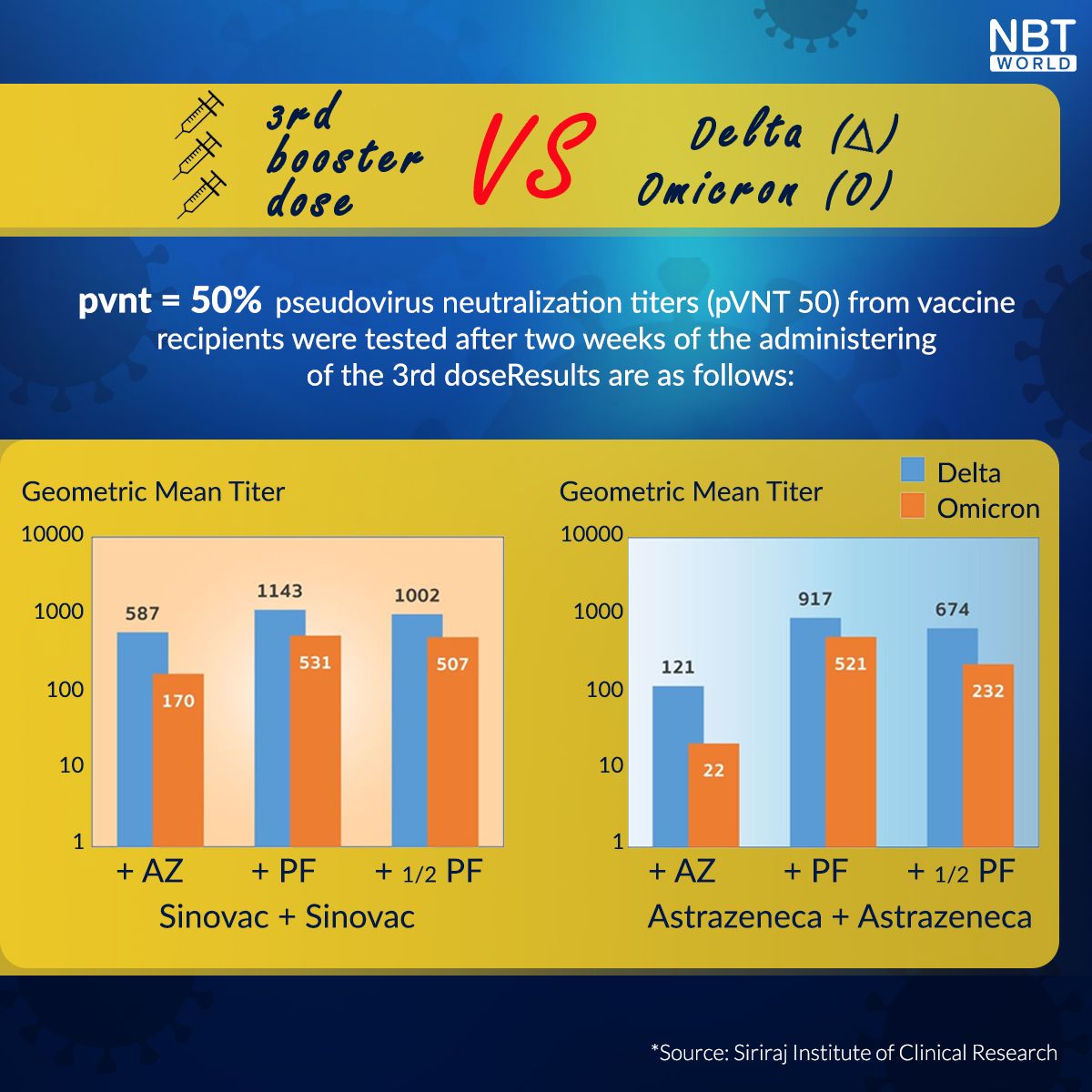
Bangkok Post: Ministry recommends boosters every 4 months
Dengue Fever
 While Thailand seems to have the corona virus under control, the situation with dengue fever, another viral disease, is extremely worrying in the Kingdom, especially during the rainy season.
Thailand's Public Health Officials advise people to make sure that there is no standing water around their homes, as this is a breeding ground for mosquitoes carrying the dengue virus.
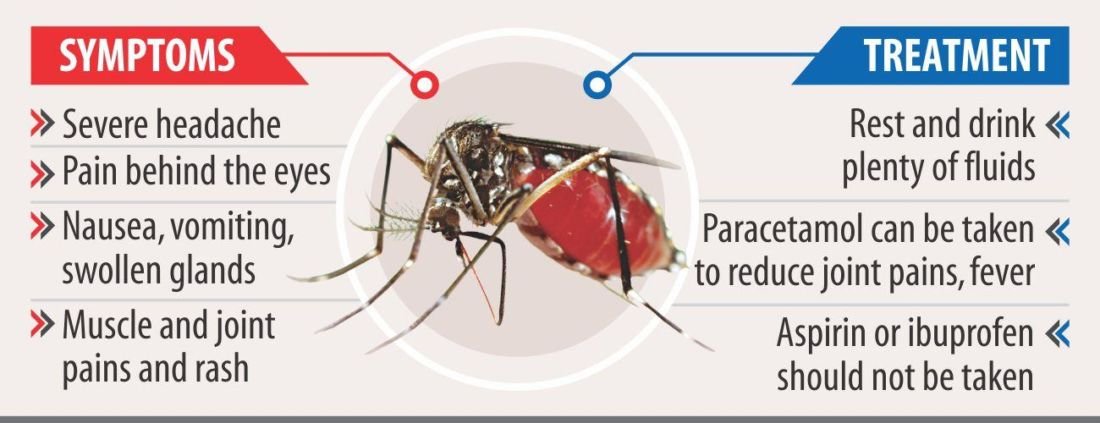
The Nation Thailand: How to fight the rising dengue threat after heavy rains
Prachatai: Struggling with mosquitoes
Prachatai: The past and present of dengue control in Thailand
The Nation: The future of dengue control
Thai Public Broadcasting Service: Public advised to be aware of dengue fever re-emergence in Thailand
Thai PBS World: Thailand's Disease Control Department is advising people to protect themselves against mosquito bites
Bangkok Post: Public warned after dengue fever spikes in January 2023; 1 dead
Bangkok Post: What to know about dengue fever as cases spread
Thai Travel Clinic: Dengue vaccine for foreigners/travelers in Thailand: Should I get it? UPDATE 2023
 Chikungunya
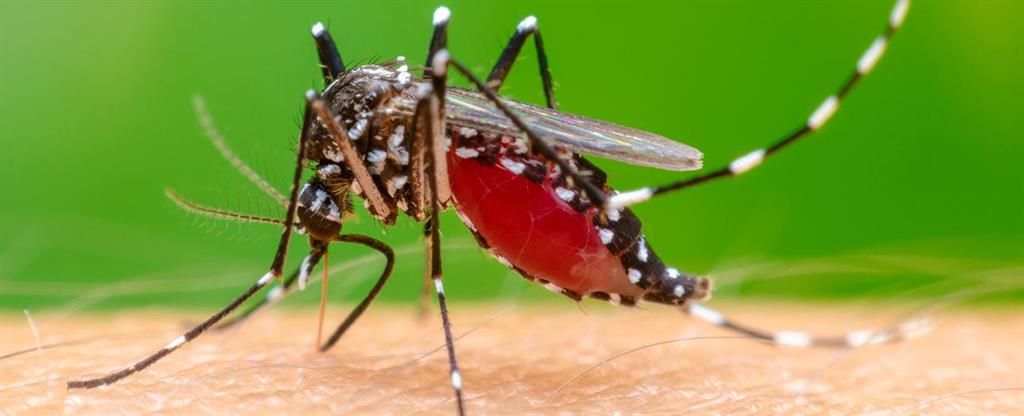 Another dangerous virus in this area is the Chikungunya virus. It is spread to people by the bite of an infected mosquito.
The most common symptoms of infection are fever and joint pain. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash.
The Chikungunya virus was found for the first time in the Americas on islands in the Caribbean in late 2013.
The virus was imported by infected travellers into new areas such as Thailand.
Currently there is no vaccine for prevention or medication to treat a Chikungunya virus infection.
Measles
 Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus.
Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than 40°C, cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms.
Measles is an airborne disease which spreads easily from one person to the next through the coughs and sneezes of infected people.
No specific treatment is available but the measles vaccine is effective at preventing the disease and is exceptionally safe.
How to kill the Viruses
Click into picture for original size
Do you know?
 What to do if the test is positive?

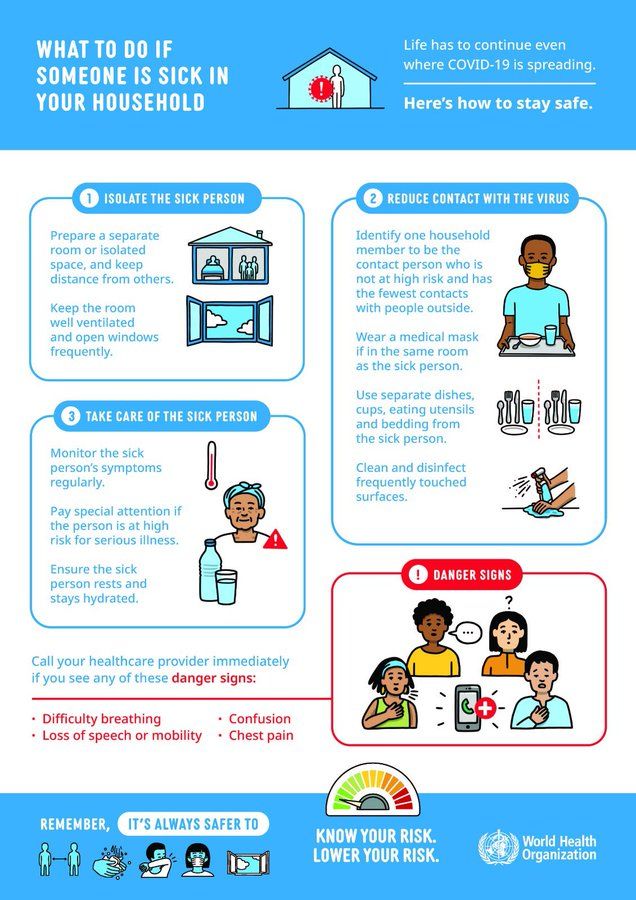 Successful vaccination

 How to dispose your masks
 |